 There is a great deal of focus on cloud-based services, platforms, and software as a service these days. The market for Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) continues to grow and mature, with new providers entering the arena and existing players continuing to expand their offerings and increase adoption by customers. If you are reading this article, you’ve probably heard or read about Infrastructure as a Service before. But do you know what it is, how it works, and whether or not it could help your organization? In this article, we will explain what IaaS is, how it differs from other types of cloud computing services like PaaS and SaaS, examples of IaaS vendors like AWS and Azure, their pros and cons for your business, who can use it effectively, and more.
There is a great deal of focus on cloud-based services, platforms, and software as a service these days. The market for Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) continues to grow and mature, with new providers entering the arena and existing players continuing to expand their offerings and increase adoption by customers. If you are reading this article, you’ve probably heard or read about Infrastructure as a Service before. But do you know what it is, how it works, and whether or not it could help your organization? In this article, we will explain what IaaS is, how it differs from other types of cloud computing services like PaaS and SaaS, examples of IaaS vendors like AWS and Azure, their pros and cons for your business, who can use it effectively, and more.
Virtual infrastructure is a term that encompasses several different cloud services. Each of these services is designed to make it easier and more affordable for businesses to build, deploy, and manage IT infrastructure. The three primary types of virtual infrastructure are virtual machine, Infrastructure as a Service, and Software as a Service. While they each provide different benefits, they all fall under the umbrella of virtual infrastructure. This article explores the principles of IaaS so that you can understand how it can benefit your organization.
When it comes to the various cloud services, there are many different options available. While some businesses may be more familiar with things like Software as a Service (SaaS) or Platform as a Service (PaaS), there are also other lesser known options such as Infrastructure as a Service. What is infrastructure as a service and how can it benefit you?
What is Infrastructure as a Service?
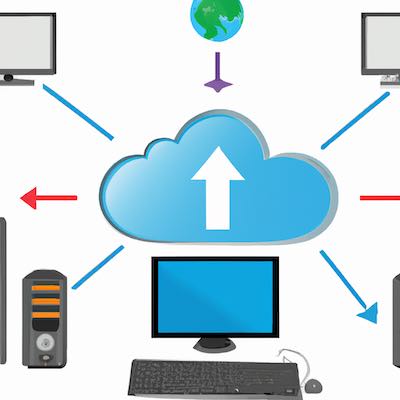
Infrastructure as a Service is a cloud computing service in which remote customers can rent virtual machines, storage, and other network resources for a specified amount of time. These virtual resources are managed by the provider and typically given to customers through a standard Open Systems Interconnect (OSI) model protocol such as Representational State Transfer (REST). IaaS providers typically offer a range of fixed configurations for customers to choose from. Customers then select the resources they need to run their specific applications. Customers are responsible for managing the operating systems, applications, and other aspects of the virtual machines they rent. IaaS providers typically provide a user interface, console, or management tool, and customers use these to create, configure, and deploy their virtual machines. IaaS is the layer where most people think about moving to the cloud. It is a virtual machine running somewhere off-premises. It is the thing most people think about when they think about cloud computing. This goes back to the idea that the cloud is a computer network that you can access remotely. With Infrastructure as a Service, you are renting access to compute resources that you can place wherever you like.
Defining IaaS and Its Core Services
IaaS provides customers with virtual machines, networking and storage, with the option of purchasing additional resources as necessary. The virtual machines are hosted in data centers maintained by the provider, and customers can access them over the internet using standard OSI-compliant network protocols. On top of these core services, providers can layer additional functionality for managing the lifecycle of the virtual machines, provisioning new ones, and connecting them with other cloud services from the same vendor or other third-party providers.
How Does IaaS Differ From Traditional Infrastructure?
Traditional physical or virtual infrastructure requires customers to procure, manage, and maintain their own hardware and software as they scale. IaaS providers provide the hardware, software, and network resources in the form of virtual machines that customers access remotely. They then manage the entire infrastructure, which frees customers up to focus on their core business. In addition to the simple fact that cloud environments are virtualized and you never have to worry about hardware, there are other benefits to Infrastructure as a Service.
Scalability - When you launch a new application, you can scale up the virtual machines that are hosting it quickly and easily. If your application’s demand suddenly spikes, you can scale up the same virtual machines again. Likewise, if demand dips temporarily, you can scale back down again.
Security - Data security is a top concern for many potential IaaS customers. But providers can offer more robust security features than many businesses can afford or implement on their own. They often use encryption and other security tools to protect your data from unauthorized access.
Resource optimization - IaaS providers can optimize the use of their resources, which means you can benefit from their experience and expertise in determining how many resources to set aside for your application.
Cost reduction - The flexibility of IaaS means you can scale up or down your virtual machine resources as necessary, which means you can avoid paying for resources you don’t need.
Simplicity - Managing your infrastructure requires a significant time investment. IaaS providers maintain a standardized environment, which makes it easier for you to launch new applications.
How Does IaaS Work?
First, you need to decide if you want a public cloud or a private cloud. Public clouds are more like traditional IaaS and allow you to access your resources from anywhere. Private clouds give you more control over your resources and where they are located. Again, there are many providers of IaaS, and the list is growing. The top providers are Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and IBM Cloud.
Why Should You Use IaaS?
IaaS is an excellent option for businesses that want to focus on their core competencies and outsource the management and maintenance of their servers and infrastructure. With IaaS, you can avoid the costs and challenges associated with hiring your own engineers to run and maintain your data centers. Companies that are building new applications can take advantage of IaaS right away, without having to make significant capital investments in new hardware and software. If your current infrastructure is struggling to keep up with demand, or if you’re simply running out of room to grow, IaaS can help.
Possible Disadvantages of Using IaaS
Like any other business technology, there are some potential drawbacks to using IaaS. For example, some providers only host applications in specific regions. It may also take longer to launch a new application if you are using an IaaS provider with high demand. Another potential drawback is the loss of control over your data. If your provider experiences a security breach that affects your data, you may lose control over it completely. If you are hosting your applications in the cloud with IaaS, you want to make sure that the provider has a good track record of keeping your data safe. If you need to scale up your applications quickly, you may experience a delay as you wait for your IaaS provider to provision new resources for you. In some cases, it may be faster to launch a new application on a virtual machine that you own that’s already fully provisioned.
Who Can Benefit from IaaS?
IaaS is a great choice for businesses that need to quickly scale up their server resources or require a short-term solution. It is also an excellent solution for businesses that want to focus on their core strengths while outsourcing their IT operations to a third-party provider. However, IaaS is suitable for a wide range of organizations and businesses. Whether you are a startup company just getting started or a large, established organization, IaaS can work for you.
Examples of IaaS Providers
There are many providers of IaaS, and the list is growing. The top providers are Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and IBM Cloud. Other providers include Rackspace, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, Cisco, Dimension Data, Fujitsu, Oracle, and many more. Some providers specialize in a particular region, so you may have to shop around to find a provider near you or one that caters to your specific needs. Also, if you are looking for a specific combination of services, such as specific machine learning or AI capabilities, you may need to contact several providers to find one that offers what you need.
Should You Use IaaS?
If you are a company that needs to quickly scale up its server resources, you might benefit from using IaaS. It is also an excellent option for companies that want to focus on their core strengths while outsourcing their IT operations to a third-party provider. IaaS is an excellent option for businesses that need to quickly scale up their server resources, or that want to focus on their core strengths while outsourcing their IT operations to a third-party provider. It may also be a good choice for companies that want to temporarily outsource their IT operations to a third-party provider while they get their operations back on track. IaaS may not be a good fit for every business. If you have a specialized application that you can’t find a provider who can host, you may have to host it yourself. Or if you need to host your application in a specific region or country, you may not be able to find a provider who can meet those requirements.